Nginx
非常好的一个讲解 nginx 的 github 仓库,作者是《深入理解 Nginx》一书的作者陶辉:https://github.com/russelltao/geektime-nginx 。
1. nginx 简介
nginx 的优点:
- 高并发,高性能
- 可扩展性好
- 高可靠性
- 热部署
- BSD 许可证
nginx 的应用场景:
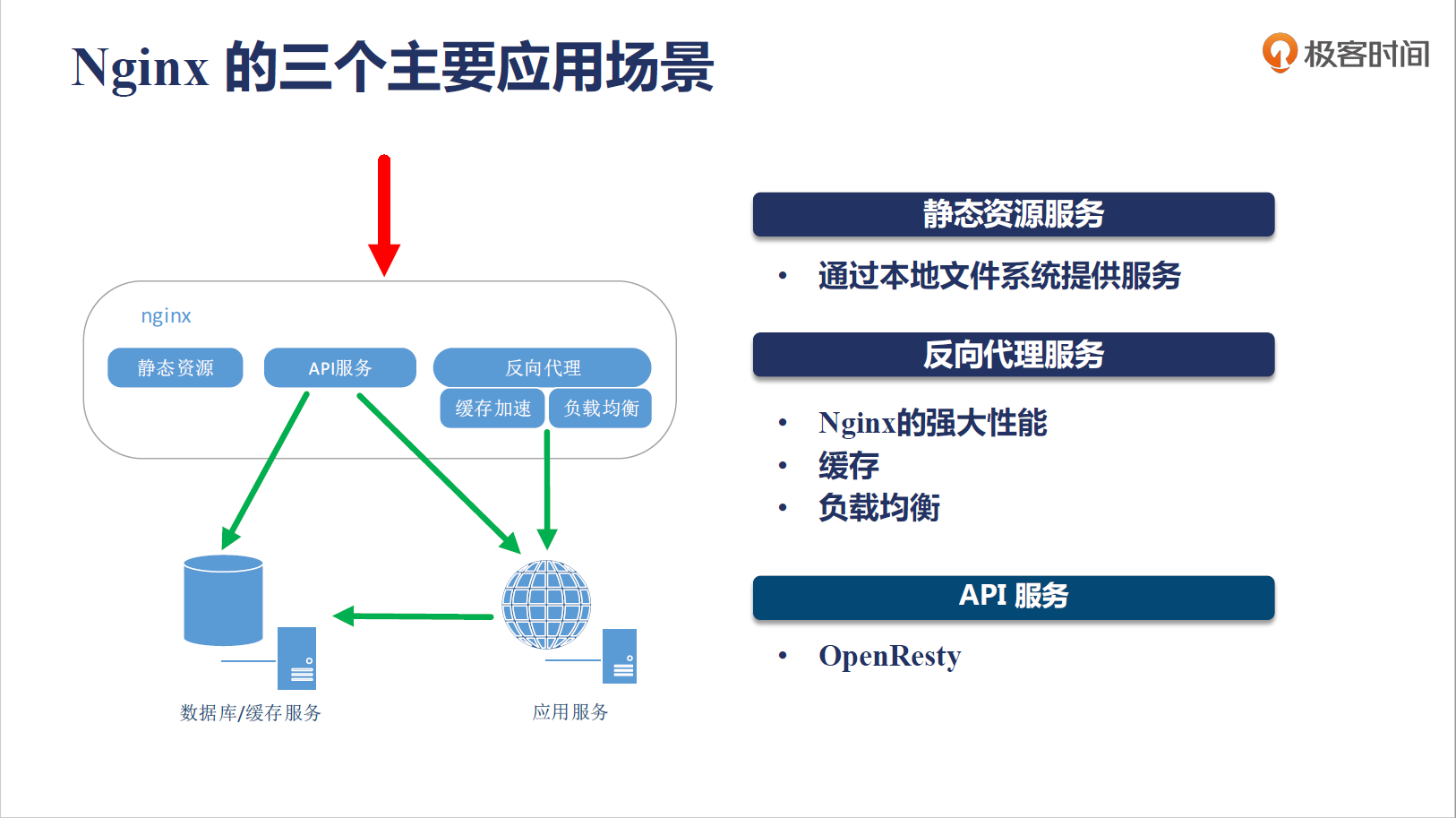
nginx 的组成:
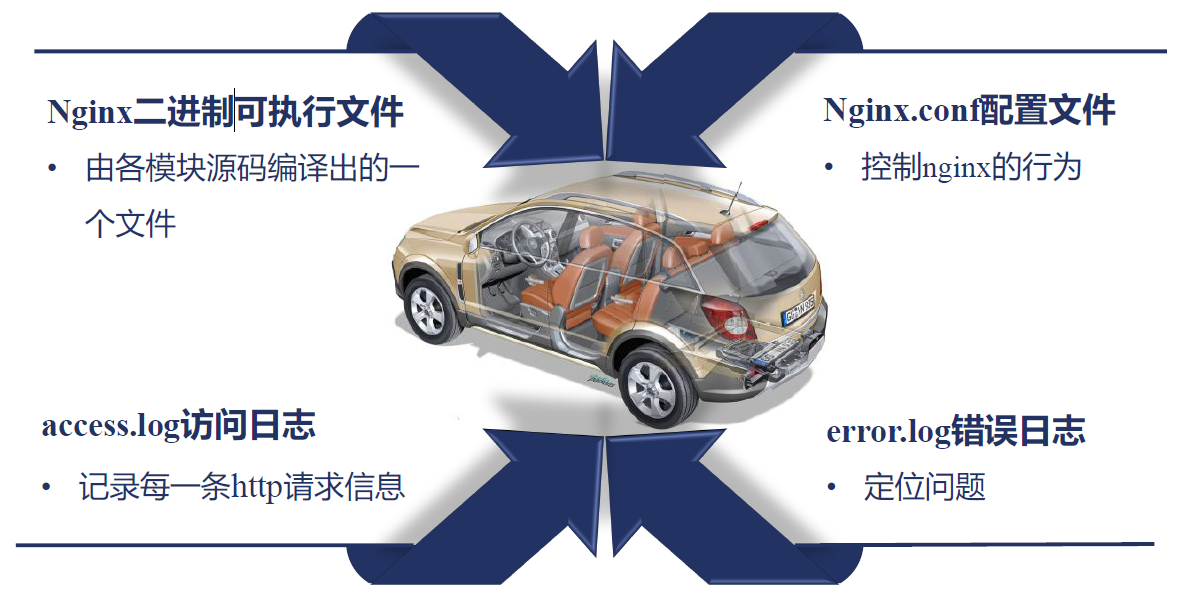
nginx 同 redis 类似都采用了 io 多路复用机制......
2. nginx 命令
通常在 nginx 的安装目录cd /usr/local/nginx中执行,命令的格式如:nginx [param] [command]
| 参数 | 格式 |
|---|---|
-? -h | 帮助 |
-c | 使用指定的配置文件 |
-g | 指定配置指令 |
-p | 指定运行目录 |
-s | 发送信号
|
-t -T | 测试配置文件是否有语法错误 |
-v -V | 打印 nginx 的版本信息、编译信息等 |
举例而言,命令如下:
| 命令 | 说明 |
|---|---|
./nginx | 启动 nginx |
./nginx -v | 查看 nginx 版本号 |
./nginx -s stop | 关闭 nginx |
./nginx -s reload | 重新加载 nginx |
3. nginx 配置文件
3.1 路径及内容
配置文件的路径:/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf,其默认的配置如下:
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log notice;
pid /var/run/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
}上述配置中引用的/etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf主要是如下的/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf:
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name localhost;
#access_log /var/log/nginx/host.access.log main;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}3.2 结构划分
... # 全局块
events {} # events 块
http { # http 块
... # http 全局块
server { # server 块
... # server 全局块
location [/] { # location 块(一个 server 块中可以有多个 location 块)
...
}
}
server {...} # 另一个 server 块(一个 http 块中可以有多个 server 块)
}
...nginx 配置文件由三大块组成:
- 全局块:配置影响 nginx 服务器全局的指令。例如运行 nginx 服务器的用户组、nginx 进程 pid 存放路径、日志存放路径、配置文件引入、允许生成的 worker process 数等。
- events 块:主要影响 nginx 服务器与用户的网络连接。例如每个进程的最大连接数、选取哪种事件驱动模型处理连接请求、是否允许同时接受多个网路连接、开启多个网络连接序列化等。
- http 块:可以嵌套多个 server,配置代理、缓存、日志等绝大多数功能,以及第三方模块的配置。例如文件引入、mime-type 定义、日志自定义、是否使用 sendfile 传输文件、连接超时时间、单连接请求数等。
- http 全局块:顾名思义。
- server 块:一个 server 相当于一台虚拟主机,nginx 可以有多台虚拟主机联合对外提供服务,这里配置虚拟主机的相关参数。一个 http 块中可以有多个 server。
- server 全局块:顾名思义。
- location 块:匹配请求的路由 uri,以及各种页面的处理情况。
- upstream 块:
3.3 语法格式
nginx 配置语法:
- 配置文件由指令与指令块构成;
- 每条指令以
;分号结尾,指令与参数间以空格符号分隔; - 指令块以
{}大括号将多条指令组织在一起; - 部分指令的参数支持正则表达式;
include语句允许组合多个配置文件以提升可维护性;- 使用
$符号使用变量; - 使用
#符号可添加注释,提高可读性。
Nginx 是由少量框架代码、大量模块构成的,其中,Nginx 框架会按照特定的语法,将配置指令读取出来,再交由模块处理。因此,Nginx 框架定义了通用的语法规则,而 Nginx 模块则定义了每条指令的语法规则,作为初学者,如果将学习目标定为掌握所有的配置指令,方向就完全错了,而且这是不可能完成的任务。
比如,ngx_http_lua_module模块定义了content_by_lua_block指令,只要它符合框架定义的{}块语法规则,哪怕大括号内是一大串 Lua 语言代码,框架也会把它交由ngx_http_lua_module模块处理。因此,下面这行指令就是合法的:
content_by_lua_block {ngx.say("Hello World ")}示例:
3.4 全局变量
nginx 有一些常用的全局变量,你可以在配置的任何位置使用它们,如下表:
| 全局变量名 | 功能 |
|---|---|
$args | 请求中的参数 |
$arg_参数名 | URL 中某个具体参数的值 |
$content_length | HTTP 请求信息里的 Content-Length |
$content_type | HTTP 请求信息里的 Content-Type |
$document_root | nginx 虚拟主机配置文件中的 root 参数对应的值 |
$document_uri | 与$uri完全相同 |
$host | 主机头,也就是域名(先从请求行中获取;如果含有 Host 头部,则用其值替换掉请求行中的主机名;如果前两者都取不到,则使用匹配上的 server_name) |
$http_头部名字 | 返回一个具体请求头部的值。大部是通用写法,几个写法特殊的为 http_host, http_user_agent, http_referer, http_via, http_x_forwarded_for, http_cookie |
$http_user_agent | 客户端的详细信息,也就是浏览器的标识,用 curl -A 可以指定 |
$http_cookie | 客户端的 cookie 信息 |
$limit_rate | 如果 nginx 服务器使用 limit_rate 配置了显示网络速率,则会显示,如果没有设置, 则显示 0 |
$query_string | 与$args完全相同 |
$remote_addr | 客户端的公网 ip |
$remote_port | 客户端的 port |
$remote_user | 由 HTTP Basic Authentication 协议传入的用户名 |
$request | 原始的 url 请求,含有方法与协议版本,例如 GET /?a=1&b=22 HTTP/1.1 |
$request_body_file | 临时存放请求包体的文件(如果包体非常小则不会存文件;client_body_in_file_only 强制所有包体存入文件,且可决定是否删除) |
$request_body | 请求中的包体,这个变量当且仅当使用反向代理,且设定用内存暂存包体时才有效 |
$request_method | 请求资源的方式,GET/POST/PUT/DELETE 等 |
$request_filename | 当前请求的资源文件的路径名称,相当于是$document_root/$document_uri的组合 |
$request_uri | 请求的链接,包括$document_uri和$args |
$scheme | 请求的协议名,如 ftp, http, https |
$server_protocol | 客户端请求资源使用的协议的版本,如 HTTP/1.0,HTTP/1.1,HTTP/2.0 等 |
$server_addr | 服务器 IP 地址 |
$server_name | 服务器的主机名 |
$server_port | 服务器的端口号 |
$uri | 请求的 URI(不同于 URL,不包括 ? 后面的请求参数) |
$http_referer | 客户端请求时的 referer,通俗讲就是该请求是通过哪个链接跳过来的,用 curl -e 可以指定 |
4. 反向代理
4.1 相关语法
4.1.1 server_name 的作用
server_name代表虚拟主机的域名。因为一个 http 块可以配置多个 server 块,即多个虚拟主机,这些虚拟主机选择兼听的端口可能相同可能不同。当端口不同时,显然通过端口即可匹配到对应的虚拟主机;当存在多个虚拟主机监听同一端口时,则需通过server_name来匹配对应的虚拟主机了。
具体而言,server_name会与 http 请求中的Host头部字段作比较,当server_name与某个Host指定的域名相匹配时,则进入对应的虚拟主机中。
当一个请求进入 nginx 时,如果匹配到多个server_name,比如通配符和正则表达式匹配,则将按以下优先级顺序:
- 完全相等的域名
- 以
*通配符开头的字符串,如果存在多个匹配最长的那一个 - 以
*通配符结尾的字符串,如果存在多个匹配最长的那一个 - 第一个匹配到的正则表达式(即按配置文件中配置的先后顺序)
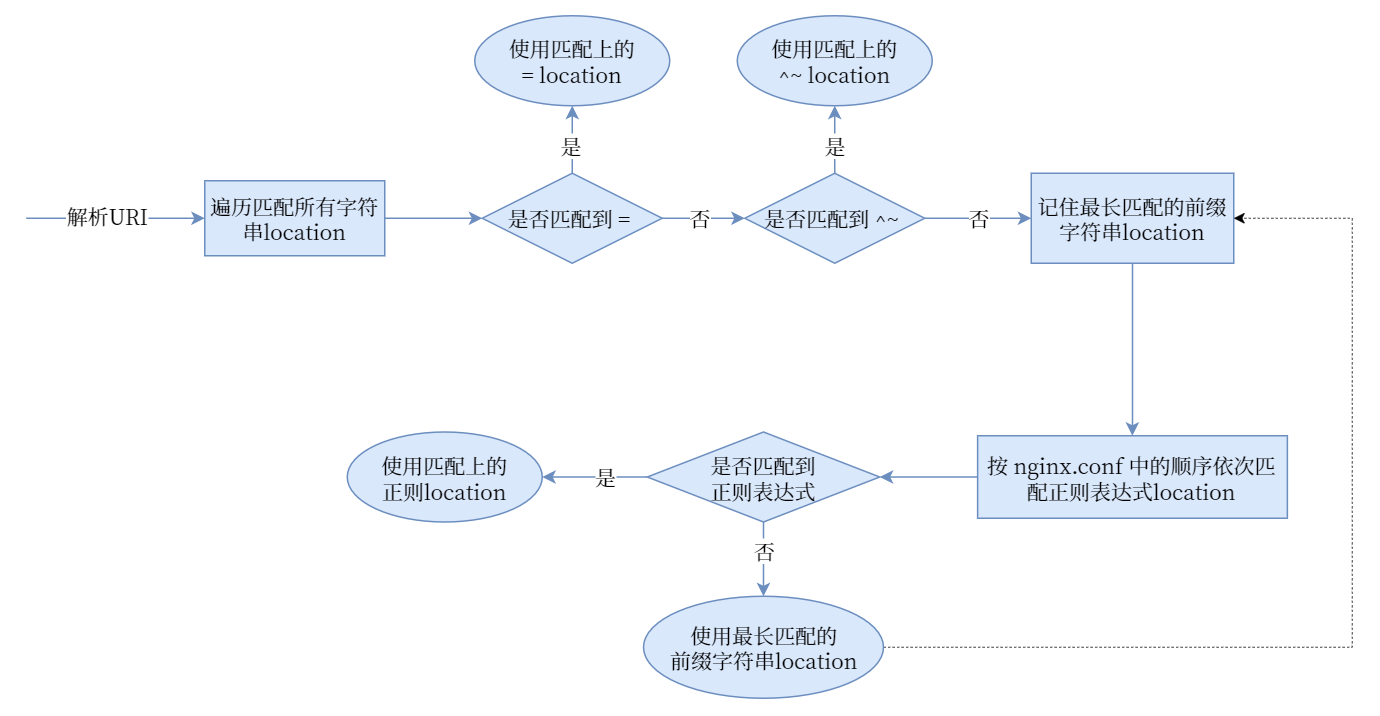
4.1.2 localtion 的 URI 匹配规则
location 的语法形式有两种:
location [=|~|~*|^~] uri { ... }:其中[=|~|~*|^~]部分为 location 修饰符(Modifier),修饰符定义了与 URI 的匹配方式;uri为 URI 的模式,可以是字符串或正则表达式。location @name { ... }
各修饰符的作用如下:
显而易见的是,location 匹配 URI 时不包含 URI 中的请求参数。
字符串匹配:
=:精准字符串匹配,只有请求的 url 路径与后面的字符串完全相等时,才会命中location = /images { root /data/web; }^~:前缀字符串匹配,匹配上后直接返回,不再向下查找location ^~ /images { root /data/web; }无修饰符:前缀字符串匹配,匹配上后继续向下查找
location /images { root /data/web; }
正则表达式匹配:
~:正则匹配,区分大小写location ~ /images/.*\.(gif|jpg|png)$ { root /data/web; }~*:正则匹配,忽略大小写location ~* \.(gif|jpg|png)$ { root /data/web; }
用于内部跳转的命名 location
@:location @images { proxy_pass http://images; }
location 的匹配顺序:
4.1.3 proxy_pass
在 nginx 中配置proxy_pass时,其后面的目标 url 后是否加有/,意义是有不同的。
以请求 http://localhost/play/hello 为例:
proxy_pass不带/时,源请求的 URI 后缀会被完整保留,直接拼接到目标 URL 的后面:server { listen 80; location ^~ /play/ { proxy_pass http://192.168.1.8:8081; # 转发为 http://192.168.1.8:8081/play/hello } }proxy_pass带有/时,源请求的 URI 后缀会抹去localtion路径中匹配到的部分,然后将剩余的部分拼接到目标 URL 的后面:server { listen 80; location ^~ /play/ { proxy_pass http://192.168.1.8:8081/; # 转发为 http://192.168.1.8:8081/hello # proxy_pass http://192.168.1.8:8081/api/; # 转发为 http://192.168.1.8:8081/api/hello # proxy_pass http://192.168.1.8:8081/api; # 转发为 http://192.168.1.8:8081/apihello } }
4.2 传递请求
当 nginx 代理请求时,它将请求发送到指定的代理服务器,获取响应,并将其发送回客户端。可以使用指定的协议将请求代理到 http 服务器或非 http 服务器。
4.2.1 转发到 http 服务器
要将请求传递给 http 代理服务器,则在一个 location 块内指定 proxy_pass 指令。 例如:
location /some/path/ {
proxy_pass http://www.example.com/link/;
}实际使用中,可以将请求转发到本机另一个服务器上,也可以根据访问的路径跳转到不同端口的服务中。例如,我们监听 9001 端口,然后把访问不同路径的请求进行反向代理:
- 把访问 http://127.0.0.1:9001/edu 的请求转发到 http://127.0.0.1:8080
- 把访问 http://127.0.0.1:9001/vod 的请求转发到 http://127.0.0.1:8081
实现方式如下,在 http 模块下增加一个 server 块:
server {
listen 9001;
location ~ /edu/ {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080;
}
location ~ /vod/ {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8081;
}
}4.2.2 转发到非 http 服务器
要将请求传递给非 HTTP 代理服务器,应使用相应的xxx_pass指令:
fastcgi_pass: 将请求传递给 FastCGI 服务器uwsgi_pass: 将请求传递给 uwsgi 服务器scgi_pass: 将请求传递给 SCGI 服务器memcached_pass: 将请求传递给 memcached 服务器
4.3 传递请求标头
默认情况下,nginx 在代理请求的Host和Connection中重新定义了两个头字段,并消除了其值为空字符串的头字段。Host设置为$proxy_host变量,Connection设置为close。
要更改这些设置,以及修改其他头字段,请使用proxy_set_header指令。 该指令可以在一个或多个位置 (location) 指定。 它也可以在特定的server上下文或http块中指定。 例如:
location /some/path/ {
proxy_set_header Host $host; # 设置 Host 字段为 $host 变量
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_pass http://localhost:8000;
}4.4 配置缓冲区
默认情况下,nginx 缓存来自代理服务器的响应,响应存储在内部缓冲区中,负责启用和禁用缓冲的指令是proxy_buffering,其默认为开启。
proxy_buffers指令控制分配给请求的缓冲区的大小和数量。来自代理服务器的响应的第一部分存储在单独的缓冲区中,其大小由proxy_buffer_size指令设置。这部分通常包含一个比较小的响应头,并且可以比其余的响应的缓冲区小。
在以下示例中,缓冲区的默认数量增加,并且响应的第一部分的缓冲区的大小小于默认值:
location /some/path/ {
proxy_buffers 16 4k;
proxy_buffer_size 2k;
proxy_pass http://localhost:8000;
}如果缓存被禁用,则在从代理服务器接收缓冲时,响应将同步发送到客户端。对于需要尽快开始接收响应的快速交互式客户端,此行为可能是可取的。
要禁用特定位置的缓冲,需要在location块中将proxy_buffering指令设置为off,如下所示:
location /some/path/ {
proxy_buffering off;
proxy_pass http://localhost:8000;
}在这种情况下,nginx 只使用由proxy_buffer_size配置的缓冲区来存储响应的当前部分。
4.5 选择传出 IP 地址
如果你的代理服务器有多个网络接口,有时你可能需要选择特定的源 IP 地址才能连接到代理服务器或上游。如果 nginx 后端的代理服务器只配置为接受来自特定 IP 网络或 IP 地址范围的连接,在这种情况下,这个配置选项就很有用。
指定proxy_bind指令和必要网络接口的 IP 地址:
location /app1/ {
proxy_bind 127.0.0.1;
proxy_pass http://example.com/app1/;
}
location /app2/ {
proxy_bind 127.0.0.2;
proxy_pass http://example.com/app2/;
}IP 地址也可以用变量指定。 例如$server_addr变量传递接受请求的网络接口的 IP 地址:
location /app3/ {
proxy_bind $server_addr;
proxy_pass http://example.com/app3/;
}4.6 其他指令
反向代理时还可以使用一些其他的指令,几个例子如下:
proxy_connect_timeout:配置 Nginx 与后端代理服务器尝试建立连接的超时时间;proxy_read_timeout:配置 Nginx 向后端服务器组发出 read 请求后,等待相应的超时时间;proxy_send_timeout:配置 Nginx 向后端服务器组发出 write 请求后,等待相应的超时时间;proxy_redirect:用于修改后端服务器返回的响应头中的 Location 和 Refresh。
5. 负载均衡
nginx 分配服务器的策略有两大类——内置策略和扩展策略:
- 内置策略:
- 轮询(默认选项)
- 加权轮询(默认权重为 1)
- IP 哈希
- 扩展策略(天马行空,取决于第三方实现):
- fair
- ......
示例配置如下:
http {
upstream myserver {
# ip_hash; # ip_hash 方式
# fair; # fair 方式
server 127.0.0.1:8081;
server 127.0.0.1:8080;
server 127.0.0.1:8082 weight=10; # weight 方式,不写默认为 1
}
server {
location / {
proxy_pass http://myserver;
proxy_connect_timeout 10;
}
}
}6. 静态资源服务器
6.1 配置示例
nginx 本身也是一个静态资源的服务器,当只有静态资源的时候,就可以使用 nginx 来做服务器,同时现在也很流行动静分离,也可以通过结合 nginx 的这部分功能来实现:
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
client_max_body_size 1024M;
location / {
root E:/wwwRoot;
index index.html;
}
}这样如果访问 http://localhost 就会访问到 E 盘 wwwRoot 目录下面的index.html,如果一个网站只是静态页面的话,那么就可以通过这种方式来实现部署。
6.2 root 与 alias
配置静态服务资源时,location 块常用root指令和alias指令,两者的区别顾名思义即可,叙述如下:
root指令指定的是资源的根路径,因此最终会用[root路径 + location路径]的规则映射静态资源请求;alias指定指定资源路径的别名,因此会使用alias的路径替换location路径,即[location路径 -> alias路径]
下面举例说明root与alias的区别:
location ^~ /test1 {
root /root/html/;
}
location ^~ /test2 {
alias /root/html/;
}- 对于 http 请求
http://ip:port/test1/web1.html,其访问的是主机上全路径为/root/html/test1/web1.html的静态资源; - 而对于请求
http://ip:port/test2/web1.html访问的是全路径为/root/html/web1.html的静态资源,其中/test2/已经被替换掉了。
6.3 js 语言描述 root 与 alias 的解析过程
细扣起来,个人疏理 root 和 alias 的生效过程,其实分别是直接的字符串拼接与直接的字符串替换,下面我们尝试用编程语言来描述这一具体过程。
首先假设有如下配置块:
location ^~ rootLocationPath {
root rootTargetPath;
}
location ^~ aliasLocationPath {
alias aliasTargetPath;
}我们用 js 语言来描述该配置块:
// 请求的 uri 部分
const uri = "/uri"; // 注意完整的 uri 是带了 / 的
// root 指令的配置
const rootLocationPath = "rootLocationPath";
const rootTargetPath = "rootTargetPath";
// alias 指令的配置
const aliasLocationPath = "aliasLocationPath";
const aliasTargetPath = "aliasTargetPath";
// 要求解的 root 指令的最终结果
let rootFinalPath = null;
// 要求解的 alias 指令的最终结果
let aliasFinalPath = null;当一个 http://ip:port/uri 进入 nginx 之后,其解析结果为:
// root 指令的最终结果其实就是两个字符串的直接拼接
rootFinalPath = `${rootTargetPath}${uri}`;
// alias 指令的最终结果是将 uri 中的 aliasLocationPath 子串替换为 aliasTargetPath 后得到的结果
aliasFinalPath = uri.replace(aliasLocationPath, aliasTargetPath);网上有很多人纠结来纠结去前前后后的/的问题,实在是走错了方向。当拼接得到最终的rootFinalPath和aliasFinalPath后,无外乎该字符串中间部分可能会少了或多了一个/。当缺少了/,路径显然是不对的;当多了/,其实最终的结果不影响,因为操作系统在解析路径时对这种冗余的斜杠/是兼容的。
6.4 结合 index 指令
使用 root 与 alias 指令 时,可搭配使用 index 指令,用来表明当 URL 中未指定具体的资源名称(xxx.html, xxx.php, xxx.xx 等)时,即 URL 只定位到了文件夹的层级,该 URL 默认指向的资源名称。index 指令的默认值为 index.html index.htm。
比如,如下配置时,访问 http://ip:port 会实际到 http://ip:port/html/haha.html
location ^~ / {
root /html;
# alias /html;
index haha.html;
}更新日志
ad16e-于8a31b-于899db-于eedbf-于c9215-于75141-于730b3-于02d25-于21f41-于a75fd-于eb17d-于73bdc-于ce390-于77d7d-于c03a1-于c74c9-于dffa4-于359ad-于
