Config
1. 问题背景
在微服务系统中,每个微服务不仅仅只有代码,还需要连接其他资源。除了项目运行的基础配置以外,还有一些配置是与我们业务有关系的,比如数据库、短信、邮件等,这些配置都是放在配置文件中管理的。
对于常规的配置管理方案而言,对于同一个微服务进行集群部署时,同一个配置相当于被复制了多份,此时如果配置需要发生修改,需要对集群中的所有节点一起进行修改,这就使事情变得相当的麻烦。综合而言,这种将配置文件散落在各个服务中的管理方式,存在以下问题:
- 管理难度大:配置文件散落在各个微服务中,难以管理。
- 安全性低:配置跟随源代码保存在代码库中,容易造成配置泄漏。
- 时效性差:微服务中的配置修改后,必须重启服务,否则无法生效。
- 局限性明显:无法支持动态调整,例如日志开关、功能开关。
由于常规配置管理的这种缺点,通常我们都会使用配置中心对配置进行统一管理,其中一种方案就是 Spring Cloud Config。
以下是 Spring Cloud Config 官方的一段自我介绍:
Spring Cloud Config provides server-side and client-side support for externalized configuration in a distributed system. ...The concepts on both client and server map identically to the Spring
EnvironmentandPropertySourceabstractions, so they fit very well with Spring applications but can be used with any application running in any language. ...The default implementation of the server storage backend uses git... It is easy to add alternative implementations and plug them in with Spring configuration.
2. Spring Cloud Config 工作原理
2.1 原理统述
Spring Cloud Config 可以将各个微服务的配置文件集中存储在一个外部的存储仓库或系统(例如 Git 、SVN 等)中,对配置的统一管理,以支持各个微服务的运行。
Spring Cloud Config 包含以下两个部分:
- Config Server:也被称为分布式配置中心,它是一个独立运行的微服务应用,用来连接配置仓库并为客户端提供获取配置信息、加密信息和解密信息的访问接口。
- Config Client:指的是微服务架构中的各个微服务,它们通过 Config Server 来管理自己的配置,并从 Config Sever 中获取和加载配置信息。
Spring Cloud Config 默认使用 Git 存储配置信息,因此使用 Spirng Cloud Config 构建的配置服务器天然就支持对微服务配置的版本管理。我们可以使用 Git 客户端工具方便地对配置内容进行管理和访问。除了 Git 外,Spring Cloud Config 还提供了对其他存储方式的支持,例如 SVN、本地化文件系统等。
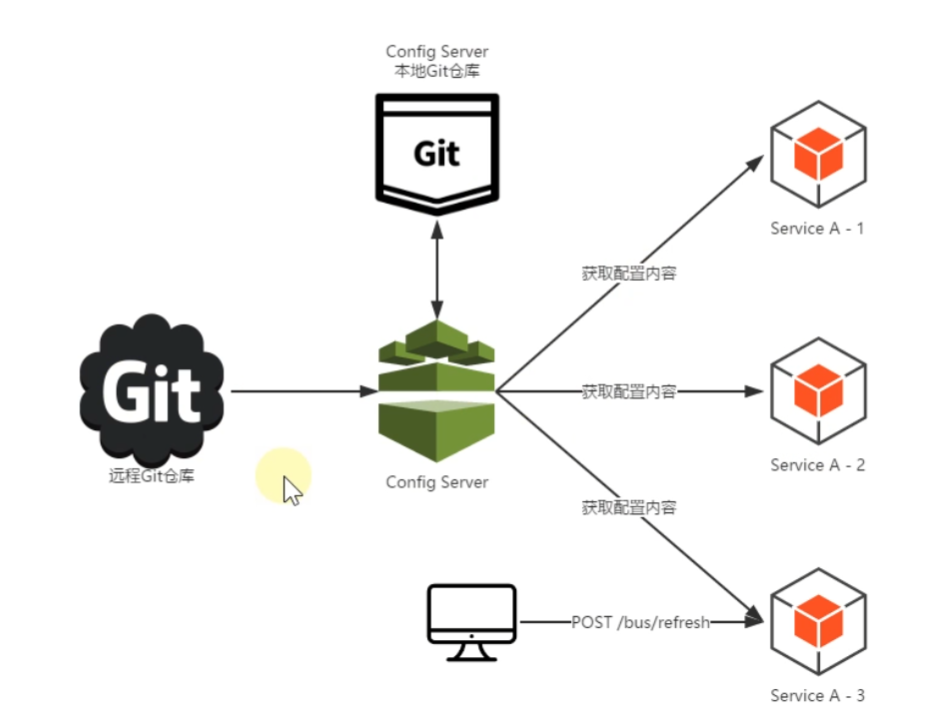
Spring Cloud Config 默认工作流程如下:
- 开发或运维人员提交配置文件到远程的 Git 仓库;
- Config 服务端(分布式配置中心)负责连接配置仓库 Git,并对 Config 客户端暴露获取配置的接口;
- Config 客户端通过 Config 服务端暴露出来的接口,拉取配置仓库中的配置;
- Config 客户端获取到配置信息,以支持服务的运行。
2.2 Config Server 的 HTTP 接口
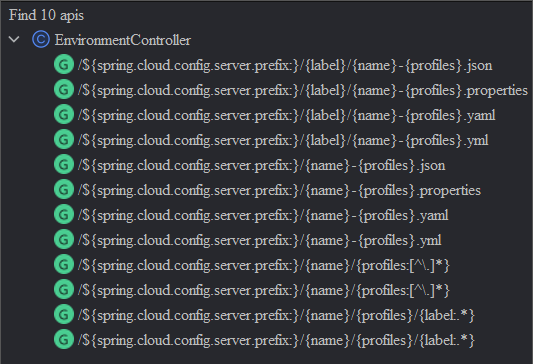
作为 Config Server,Spring Cloud Config 通过一个 org.springframework.cloud.config.server.environment.EnvironmentController 给客户端提供了如下获取配置文件的 HTTP 接口(其获取的响应目标都是org.springframework.cloud.config.environment.Environment):
| 访问规则 | 示例 |
|---|---|
GET /{application}/{profile}[/{label}] | /myApp/dev/master |
GET /{application}-{profile}.{suffix} | /myApp-dev.yml |
GET /{label}/{application}-{profile}.{suffix} | /master/myApp-dev.yml |
接口内各参数说明如下:
{application}:客户端应用名称,如myApp{profile}:环境名,比如一个项目通常都有开发(dev)环境、测试(test)环境、生产(prod)环境,在找配置文件时会与{application}拼接形成{application}-{profile},例如myApp-dev.yml、myApp-test.yaml、myApp-prod.properties等;{label}:当使用 Git 管理配置文件时,意为 Git 分支名;当使用本地文件系统管理配置文件时,意为子目录名;{suffix}:对于一个配置文件,希望以什么格式返回其数据。例如配置中心存在一个myApp-dev.yml配置文件,如果suffix传入properties,则 Config Server 会将配置文件转换为properties格式的文本返回。其可选项为yml, yaml, properties, json
官方文档 有过这样一段大概的描述:
where
applicationis injected as thespring.config.namein theSpringApplication(what is normallyapplicationin a regular Spring Boot app),profileis an active profile (or comma-separated list of properties), andlabelis an optional git label (defaults tomaster.)
如果去看EnvironmentController中的 url,会发现其中的路径参数在表达application的时候,是用的变量名name:
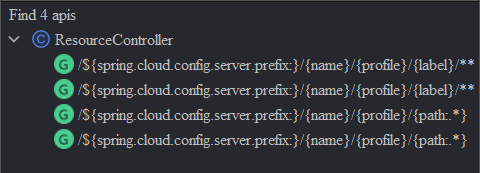
在看spring-cloud-config-server包的时候,发现其中还有一个ResourceController,不知道具体做啥用的,这里暂记一下吧。其内的 url 包含如下:
3. 快速入门
3.1 配置中心
Git 仓库地址:spring-cloud-config-file: spring cloud config 配置文件仓库 - Gitee.com。其目录大概长这样:
$ tree .
.
├── config-client1-dev.yml
├── config-client1-test.yml
├── config-client1.yml
├── config-client2-dev.yml
├── config-client2-test.yml
└── config-client2.yml
0 directories, 6 files3.2 服务端
pom
<artifactId>config-server</artifactId> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> </dependencies>application.yml
server: port: 8888 spring: cloud: config: server: git: uri: git@gitee.com:chua-n/play-spring-cloud-config.git启动类
@EnableConfigServer @SpringBootApplication public class ConfigServerApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ConfigServerApplication.class, args); } }
3.3 客户端
客户端 1 号
pom
<artifactId>config-client1</artifactId> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies>application.yml
spring: application: name: config-client1 profiles: active: test config: import: optional:configserver:http://localhost:8888 cloud: config: label: main name: config-client3,config-client2,${spring.application.name}启动类
@SpringBootApplication public class ConfigClient1Application implements InitializingBean { @Value("${env.profile:default}") private String curProfile; @Value("${server.port}") private int port; @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() { System.out.println(); System.out.printf("curProfile: %s, port: %d\n", curProfile, port); System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ConfigClient1Application.class, args); } }
客户端 2 号
pom
<artifactId>config-client2</artifactId> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies>application.yml
spring: application: name: config-client2 profiles: active: dev config: import: optional:configserver:http://localhost:8888启动类
@SpringBootApplication public class ConfigClient2Application implements InitializingBean { @Value("${env.profile:default}") private String curProfile; @Value("${server.port}") private int port; @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() { System.out.println(); System.out.printf("curProfile: %s, port: %d\n", curProfile, port); System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ConfigClient2Application.class, args); } }
4. Environment Repository
官方文档 Environment Repository。
4.1 概念介绍
Where should you store the configuration data for the Config Server? The strategy that governs this behaviour is the EnvironmentRepository, serving Environment objects. This Environment is a shallow copy of the domain from the Spring Environment. The Environment resources are parametrized by three variables:
{application}, which maps tospring.application.nameon the client side.{profile}, which maps tospring.profiles.activeon the client (comma-separated list).{label}, which is a server side feature labelling a "versioned" set of config files.(注意这个 versioned 在表达一个抽象性的概念)
Repository implementations generally behave like a Spring Boot application, loading configuration files from a spring.config.name equal to the {application} parameter, and spring.profiles.active equal to the {profiles} parameter. Precedence rules for profiles are also the same as in a regular Spring Boot application: Active profiles take precedence over defaults, and, if there are multiple profiles, the last one wins (similar to adding entries to a Map).
EnvironmentRepository源码:package org.springframework.cloud.config.server.environment; import org.springframework.cloud.config.environment.Environment; /** * @author Dave Syer * @author Roy Clarkson */ public interface EnvironmentRepository { Environment findOne(String application, String profile, String label); default Environment findOne(String application, String profile, String label, boolean includeOrigin) { return findOne(application, profile, label); } }Environment源码:package org.springframework.cloud.config.environment; import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonCreator; import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonProperty; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; public class Environment { public static final String SLASH_PLACEHOLDER = "(_)"; private String name; private String[] profiles; private String label; private List<PropertySource> propertySources; private String version; private String state; public Environment(String name, String... profiles) { this(name, profiles, "master", (String)null, (String)null); } public Environment(Environment env) { this(env.getName(), env.getProfiles(), env.getLabel(), env.getVersion(), env.getState()); } @JsonCreator public Environment(@JsonProperty("name") String name, @JsonProperty("profiles") String[] profiles, @JsonProperty("label") String label, @JsonProperty("version") String version, @JsonProperty("state") String state) { this.profiles = new String[0]; this.propertySources = new ArrayList(); this.name = name; this.profiles = profiles; this.label = label; this.version = version; this.state = state; } // ... }
EnvironmentRepository有很多实现类,我们所说的 Spring Cloud Config 支持多种形式的配置文件管理方式,其实就是通过EnvironmentRepository接口的实现类来做到的。比如 Git 的 JGitEnvironmentRepository,SVN 的SvnKitEnvironmentRepository,本地文件系统的NativeEnvironmentRepository。
4.2 Git Backend
详见官方文档 Git Backend。
The default implementation of EnvironmentRepository uses a Git backend, which is very convenient for managing upgrades and physical environments and for auditing changes.
To change the location of the repository, you can set the spring.cloud.config.server.git.uri configuration property in the Config Server (for example in application.yml). If you set it with a file: prefix, it should work from a local repository so that you can get started quickly and easily without a server.
This repository implementation maps the {label} parameter of the HTTP resource to a git label (commit id, branch name, or tag).
- If the git branch or tag name contains a slash (
/), then the label in the HTTP URL should instead be specified with the special string(_)(to avoid ambiguity with other URL paths).- For example, if the label is
foo/bar, replacing the slash would result in the following label:foo(_)bar.
- For example, if the label is
- The inclusion of the special string
(_)can also be applied to the{application}parameter. If you use a command-line client such as curl, be careful with the brackets in the URL — you should escape them from the shell with single quotes (''). - The default label used for Git is
main. If you do not setspring.cloud.config.server.git.defaultLabeland a branch namedmaindoes not exist, the config server will by default also try to checkout a branch namedmaster. If you would like to disable to the fallback branch behavior you can setspring.cloud.config.server.git.tryMasterBranchtofalse.
4.3 File System Backend
详见官方文档 File System Backend。
Spring Cloud Config 也支持从本地的classpath或者文件系统来管理配置文件(对应实现类为NativeEnvironmentRepository):
- To use the native profile, launch the Config Server with
spring.profiles.active=native; - 存储配置文件的具体目录位置通过
spring.cloud.config.server.native.searchLocations属性来指定。
关于 searchLocations 属性:
searchLocations的默认值与一个单体 Spring Boot 项目的配置文件搜索路径相同,即[classpath:/, classpath:/config, file:./, file:./config]。需要强调的一点是,这并不会将 config server 本身的application.properties配置文件暴露给 config client,因为 server 端在向 client 端发送 property sources 前会移除掉 server 自身的配置文件。对于某一个名称的配置文件,当其位于多个搜索路径中时,
searchLocations中后出现的搜索路径的优先级更高。在指定搜索路径时记得加上
file:前缀,因为如果不加的话默认会从classpath找;此外,在使用file:时,注意 Windows 系统下需要一个额外的/来指定根路径,例如file:///${user.home}/config-repo。就像任何 Spring Boot 应用一样,搜索路径中可以使用
${}形式的变量。搜索路径中可以包含
{application}、{profile}、{label}三个特殊的占位符。In this way, you can segregate the directories in the path and choose a strategy that makes sense for you (such as subdirectory per application or subdirectory per profile).
如果你没有在搜索路径上放置占位符,
NativeEnvironmentRepository也依然会在搜索路径的末尾加上客户端请求传过来的{label}参数,最终而言,会在每一个(原始的)搜索路径以及该路径中加了/{label}/后缀的子文件夹中进行配置文件的搜索(the labelled properties take precedence in the Spring Environment)。- Thus, the default behaviour with no placeholders is the same as adding a search location ending with
/{label}/. - For example,
file:/tmp/configis the same asfile:/tmp/config,file:/tmp/config/{label}. - This behavior can be disabled by setting
spring.cloud.config.server.native.addLabelLocations=false.
- Thus, the default behaviour with no placeholders is the same as adding a search location ending with
5. Embedding the Config Server
The Config Server runs best as a standalone application. However, if need be, you can embed it in another application. To do so, use the @EnableConfigServer annotation.
An optional property named spring.cloud.config.server.bootstrap can be useful in this case. It is a flag to indicate whether the server should configure itself from its own remote repository. By default, the flag is off, because it can delay startup. However, when embedded in another application, it makes sense to initialize the same way as any other application. When setting spring.cloud.config.server.bootstrap to true you must also use a composite environment repository configuration. For example
spring:
application:
name: configserver
profiles:
active: composite
cloud:
config:
server:
composite:
- type: native
search-locations: ${HOME}/Desktop/config
bootstrap: trueIf you use the bootstrap flag, the config server needs to have its name and repository URI configured in
bootstrap.yml.
To change the location of the server endpoints, you can (optionally) set spring.cloud.config.server.prefix (for example, /config), to serve the resources under a prefix. The prefix should start but not end with a /. It is applied to the @RequestMappings in the Config Server (that is, underneath the Spring Boot server.servletPath and server.contextPath prefixes).
If you want to read the configuration for an application directly from the backend repository (instead of from the config server), you basically want an embedded config server with no endpoints. You can switch off the endpoints entirely by not using the @EnableConfigServer annotation (set spring.cloud.config.server.bootstrap=true).
6. Push Notifications and Spring Cloud Bus
略,详见官方文档 Push Notifications and Spring Cloud Bus 。
7. Config Client 的配置详解
7.1 连接配置服务
Spring Boot Config Data 的方式
Spring Boot 2.4 introduced a new way to import configuration data via the spring.config.import property. This is now the default way to bind to Config Server.
To optionally connect to config server set the following in application.properties:
spring.config.import=optional:configserver:This will connect to the Config Server at the default location of
http://localhost:8888.Removing the
optional:prefix will cause the Config Client to fail if it is unable to connect to Config Server.To change the location of Config Server either set
spring.cloud.config.urior add the url to thespring.config.importstatement such as,spring.config.import=optional:configserver:http://myhost:8888.The location in the import property has precedence over the uri property.
在这种方式下,客户端不需要使用bootstrap文件,无论 yml 形式的还是 properties 形式的。快速入门中直接使用的就是这种方式。
Bootstrap 的方式
客户端如果要使用传统的bootstrap方式来连接 config server,必须通过以下两种方式之一:
- 引入
spring-cloud-starter-bootstrapstarter 依赖; - 设置属性
spring.cloud.bootstrap.enabled=true,必须通过系统属性或者环境变量来设置。- Once bootstrap has been enabled any application with Spring Cloud Config Client on the classpath will connect to Config Server as follows: When a config client starts, it binds to the Config Server (through the
spring.cloud.config.uribootstrap configuration property) and initializes SpringEnvironmentwith remote property sources. - The net result of this behavior is that all client applications that want to consume the Config Server need a
bootstrap.yml(or an environment variable) with the server address set inspring.cloud.config.uri(it defaults tohttp://localhost:8888).
- Once bootstrap has been enabled any application with Spring Cloud Config Client on the classpath will connect to Config Server as follows: When a config client starts, it binds to the Config Server (through the
我们以快速入门中的客户端 2 号为例,做如下更改即可:
启动类:
@SpringBootApplication public class ConfigClient2Application implements InitializingBean { @Value("${env.profile:default}") private String curProfile; @Value("${server.port}") private int port; @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() { System.out.println(); System.out.printf("curProfile: %s, port: %d\n", curProfile, port); System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { System.setProperty("spring.cloud.bootstrap.enabled", String.valueOf(true)); SpringApplication.run(ConfigClient2Application.class, args); } }application.yml直接改为名bootstrap.yml,文件内容不变,依赖如下:spring: application: name: config-client2 profiles: active: dev config: import: optional:configserver:http://localhost:8888上述改名后,未修改配置文件本身的内容,事实上,按照上述文档描述,可以不使用
spring.config.import属性,选择配置spring.cloud.config.uri也可:spring: application: name: config-client2 profiles: active: dev cloud: config: uri: http://localhost:8888
服务发现的方式
If you use a DiscoveryClient implementation, such as Spring Cloud Netflix and Eureka Service Discovery or Spring Cloud Consul, you can have the Config Server register with the Discovery Service.
略,详见官方文档 Discovery First Lookup。
7.2 查找远程配置文件
The Config Service serves property sources from /{application}/{profile}/{label}, where the default bindings in the client app are as follows:
You can override all of them by setting
spring.cloud.config.*(where*isname,profileorlabel).
{application}:${spring.application.name}When setting the property
${spring.application.name}do not prefix your app name with the reserved wordapplication-to prevent issues resolving the correct property source.{profile}:${spring.profiles.active}(actuallyEnvironment.getActiveProfiles()){label}:masterThe
labelis useful for rolling back to previous versions of configuration. With the default Config Server implementation, it can be a git label, branch name, or commit ID.Label can also be provided as a comma-separated list. In that case, the items in the list are tried one by one until one succeeds.
This behavior can be useful when working on a feature branch. For instance, you might want to align the config label with your branch but make it optional (in that case, use
spring.cloud.config.label=myfeature,develop).
客户端程序是通过 org.springframework.cloud.config.client.ConfigServicePropertySourceLocator 的 getRemoteEnvironment 方法来发送配置文件的获取请求的。
7.3 安全问题
略,详见官方文档 Security。
更新日志
a357e-于899db-于eedbf-于c9215-于75141-于730b3-于21f41-于2e4cf-于5d409-于628bb-于39993-于8025a-于91293-于8ea31-于10f7f-于
