Zookeeper
1. Zookeeper
1.1 概念
Zookeeper 是 Apache Hadoop 项目下的一个子项目,是一个树形目录服务。Zookeeper 翻译过来就是动物园管理员,它是用来管 Hadoop(大象)、Hive(大象)、Pig(小猪)的管理员,简称 ZK。
ZK 是一个分布式的、开源的分布式应用程序的协调服务。其提供的主要功能包括:
- 配置管理
- 分布式锁
- 集群管理
1.2 安装
zk 是用 Java 写的,去官网 Apache ZooKeeper 下载解压就可以了。
1.3 数据模型
ZK 是一个树形目录服务,其数据模型和 Unix 的文件系统目录树很类似,拥有一个层次化结构。
| Unix | ZK |
|---|---|
.png) | .png) |
- 其中每一个节点都被称为
ZNode,每个节点上都会保存自己的数据和节点信息。 - 节点可以拥有子节点,同时也允许少量(默认 1MB)数据存储在该节点之下。
ZNode可以分为四大类:PERSISTENT:持久化节点。这类节点被创建后,就会一直存在于 Zk 服务器上。直到手动删除。PERSISTENT_SEQUENTIAL:持久化顺序节点,-s。它的基本特性同持久节点,不同在于增加了顺序性。父节点会维护一个自增整性数字,用于子节点的创建的先后顺序。EPHEMERAL:临时节点,-e。临时节点的生命周期与客户端的会话绑定,一旦客户端会话失效(并非指 TCP 连接断开),那么这个节点就会被自动清理掉。zk 规定临时节点只能作为叶子节点。EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL:临时顺序节点,-es。基本特性同临时节点,添加了顺序的特性。
Znode 数据节点的代码如下,其中包含了「存储数据、访问权限、子节点引用、节点状态信息」:
public class DataNode implements Record {
byte data[];
Long acl;
public StatPersisted stat;
private Set<String> children = null;
}- 「data」:znode 存储的业务数据信息
- 「ACL」:记录客户端对 znode 节点的访问权限,如 IP 等。
- 「child」:当前节点的子节点引用
- 「stat」:包含 Znode 节点的状态信息,比如 「事务 id、版本号、时间戳」 等等。
1.4 监听机制
Watcher 监听机制
Zookeeper 允许客户端向服务端的某个 Znode 注册一个 Watcher 监听,当服务端的一些指定事件触发了这个 Watcher,服务端会向指定客户端发送一个事件通知来实现分布式的通知功能,然后客户端根据 Watcher 通知状态和事件类型做出业务上的改变。
可以把 Watcher 理解成客户端注册在某个 Znode 上的触发器,当这个 Znode 节点发生变化时(增删改查),就会触发 Znode 对应的注册事件,注册的客户端就会收到异步通知,然后做出业务的改变。
Watcher 监听机制的工作原理
- ZooKeeper 的 Watcher 机制主要包括客户端线程、客户端 WatcherManager、Zookeeper 服务器三部分。
- 客户端向 ZooKeeper 服务器注册 Watcher 的同时,会将 Watcher 对象存储在客户端的 WatchManager 中。
- 当 zookeeper 服务器触发 watcher 事件后,会向客户端发送通知, 客户端线程从 WatcherManager 中取出对应的 Watcher 对象来执行回调逻辑。
Watcher 特性总结
- 「一次性」: 一个 Watch 事件是一个一次性的触发器。一次性触发,客户端只会收到一次这样的信息。
- 「异步的」 :Zookeeper 服务器发送 watcher 的通知事件到客户端是异步的,不能期望能够监控到节点每次的变化,Zookeeper 只能保证最终的一致性,而无法保证强一致性。
- 「轻量级」: Watcher 通知非常简单,它只是通知发生了事件,而不会传递事件对象内容。
- 「客户端串行」: 执行客户端 Watcher 回调的过程是一个串行同步的过程。
- 注册 watcher 用 getData、exists、getChildren 方法
- 触发 watcher 用 create、delete、setData 方法
1.5 ZK 命令
服务端命令
| 服务端命令 | 作用 |
|---|---|
./zkServer.sh start | 启动 zk 服务 |
./zkServer.sh status | 查看 zk 服务状态 |
./zkServer.sh stop | 停止 zk 服务 |
./zkServer.sh restart | 重启 zk 服务 |
客户端命令
| 客户端常用命令 | 作用 |
|---|---|
./zkCli.sh -server ip:port | 连接 zk 服务端 |
quit | 断开连接 |
help | 查看命令帮助 |
ls [-s, -w, -R] /node_path | 显示指定目录下的节点 |
create [-e, -s, -es] /node_path value | 创建持久化(临时、持久化顺序、临时顺序)节点 |
get /node_path | 获取节点值 |
set /node_path value | 设置节点值 |
delete /node_path | 删除单个节点 |
deleteall /node_path | 删除带有子节点的节点 |
1.6 Java API
常见的 zk Java API 有:
- 原生 Java API:官方的,很难用
- ZkClient:对官方的进行了一些封装,依旧不好用
- Curator:原本由 netflix 公司研发,后捐献给 Apache 基金会,目前是 Apache 的顶级项目
Curator 简化了 zk 客户端的使用,其官网是 http://curator.apache.org/。
Curaotr 的 Maven 依赖坐标主要为:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId>
<artifactId>curator-framework</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId>
<artifactId>curator-recipes</artifactId>
</dependency>1.7 zk 分布式锁
Zookeeper 是使用临时顺序节点特性实现分布式锁的:
- 获取锁:创建临时节点,检查序号最小
- 释放锁:删除临时节点,监听通知
获取锁
当第一个客户端请求过来时,Zookeeper 客户端会创建一个持久节点 /locks。如果它(Client1)想获得锁,需要在 locks 节点下创建一个顺序节点 lock1。如图:
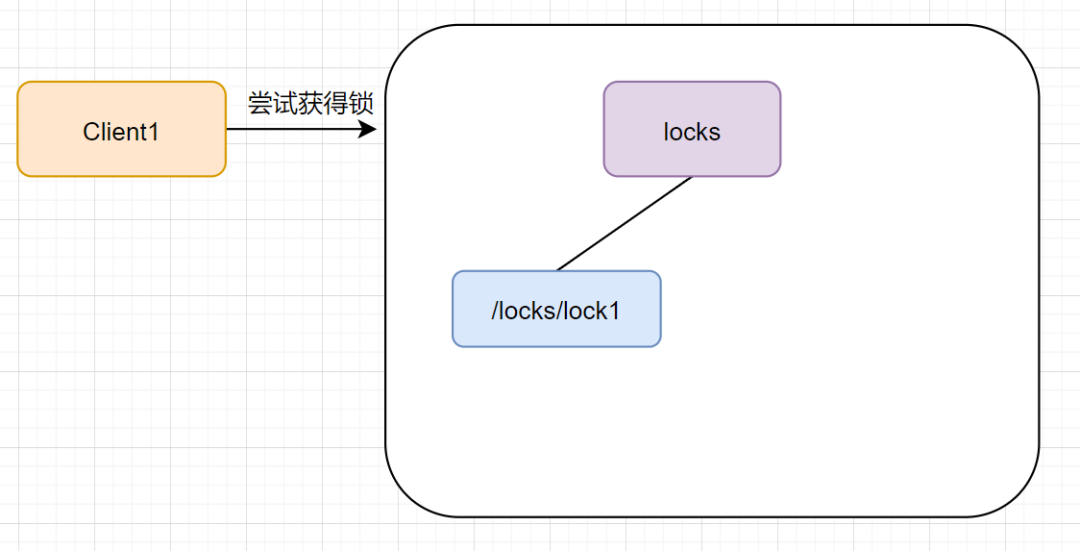
接着,客户端 Client1 会查找 locks 下面的所有临时顺序子节点,判断自己的节点 lock1 是不是排序最小的那一个,如果是,则成功获得锁。如图:
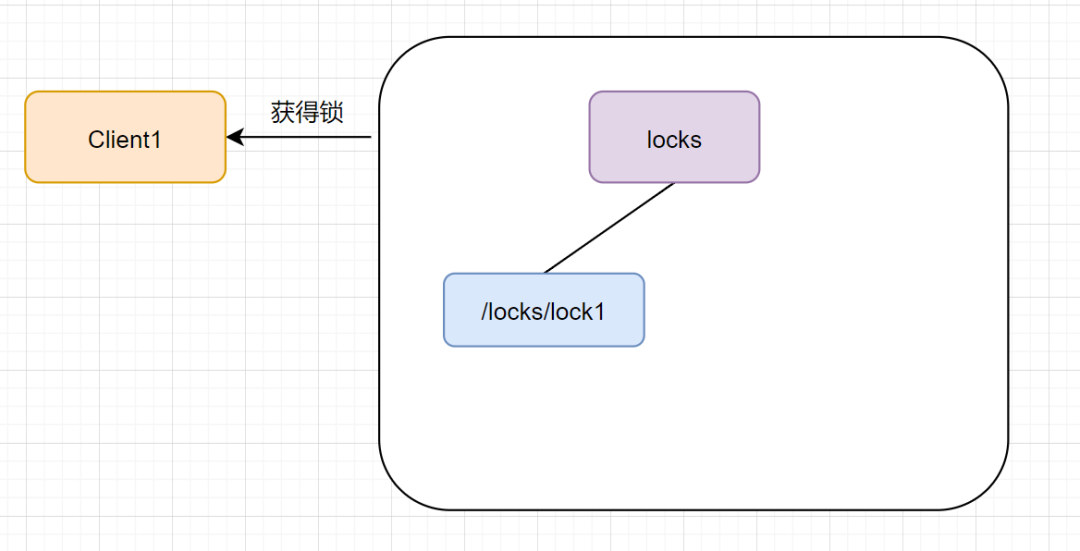
这时候如果又来一个客户端 client2 前来尝试获得锁,它会在 locks 下再创建一个临时节点 lock2:
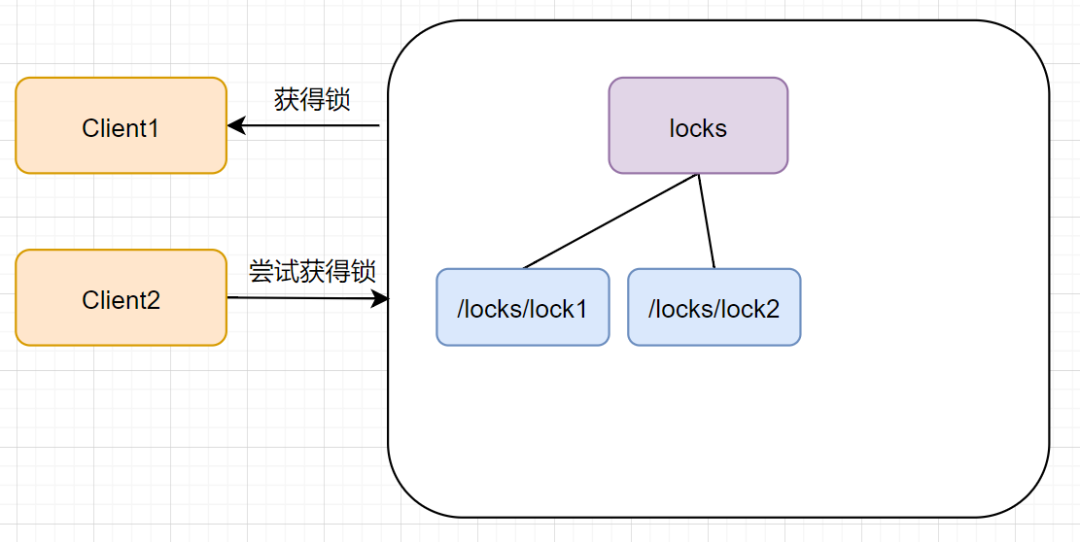
客户端 client2 一样也会查找 locks 下面的所有临时顺序子节点,判断自己的节点 lock2 是不是最小的,此时,发现 lock1 才是最小的,于是获取锁失败。获取锁失败,它是不会甘心的,client2 向它排序靠前的节点 lock1 注册 Watcher 事件,用来监听 lock1 是否存在,也就是说 client2 抢锁失败进入等待状态。如下图:
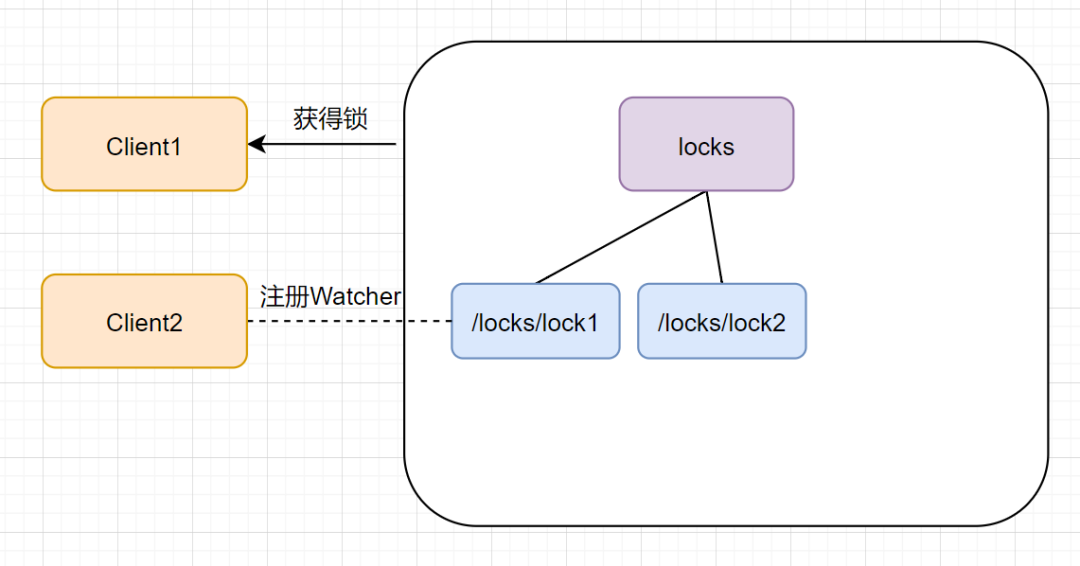
此时,如果再来一个客户端 Client3 来尝试获取锁,它会在 locks 下再创建一个临时节点 lock3。如下图:
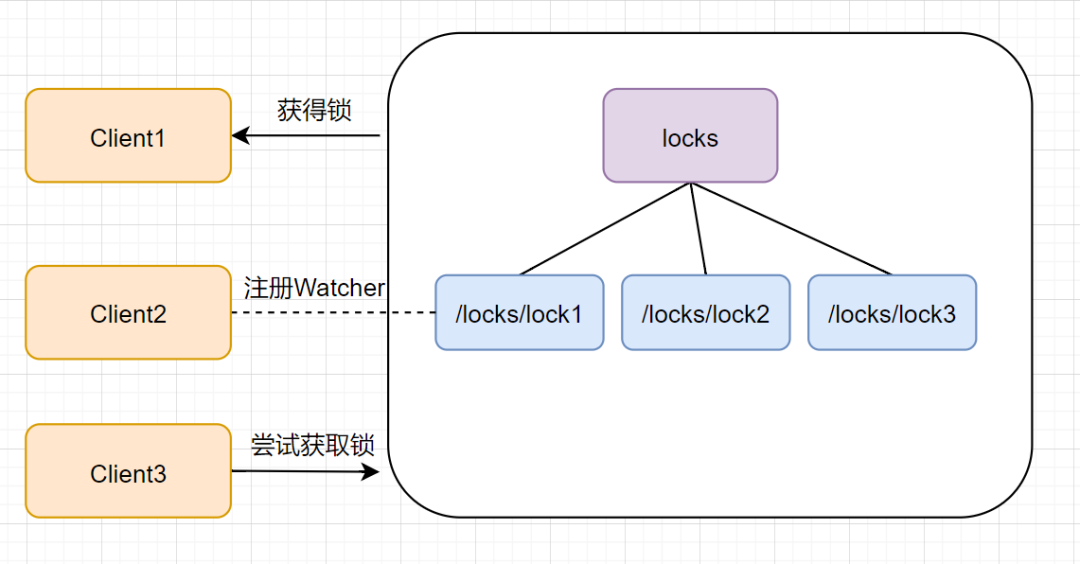
同样地,client3 一样也会查找 locks 下面的所有临时顺序子节点,判断自己的节点 lock3 是不是最小的,发现自己不是最小的,就获取锁失败。它也是不会甘心的,它会向在它前面的节点 lock2 注册 Watcher 事件,以监听 lock2 节点是否存在。如下图:
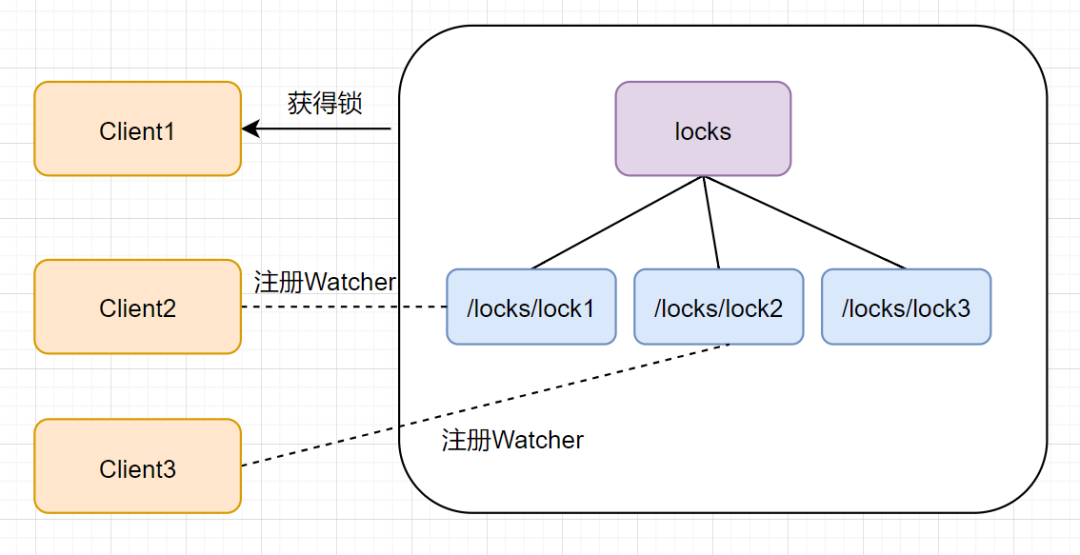
释放锁
zookeeper 的「客户端业务完成或者故障」,都会删除临时节点,释放锁。如果是任务完成,Client1 会显式调用删除 lock1 的指令,如下图:
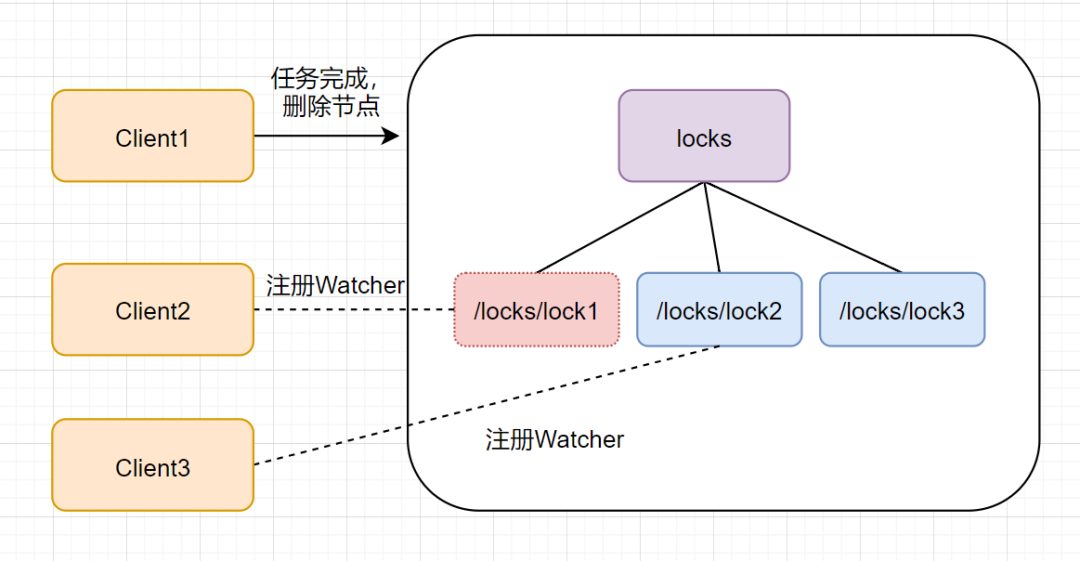
如果是客户端故障了,根据临时节点的特性,lock1 是会自动删除的,如下图:
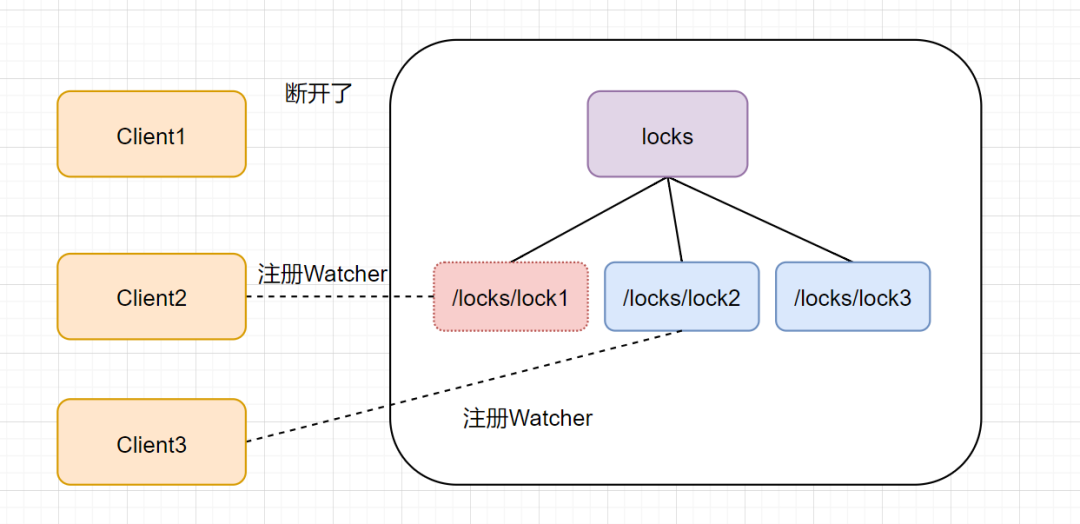
lock1 节点删除,Client2 立刻收到通知,也会查找 locks 下面的所有临时顺序子节点,发现 lock2 是最小,就获得锁,如下图:
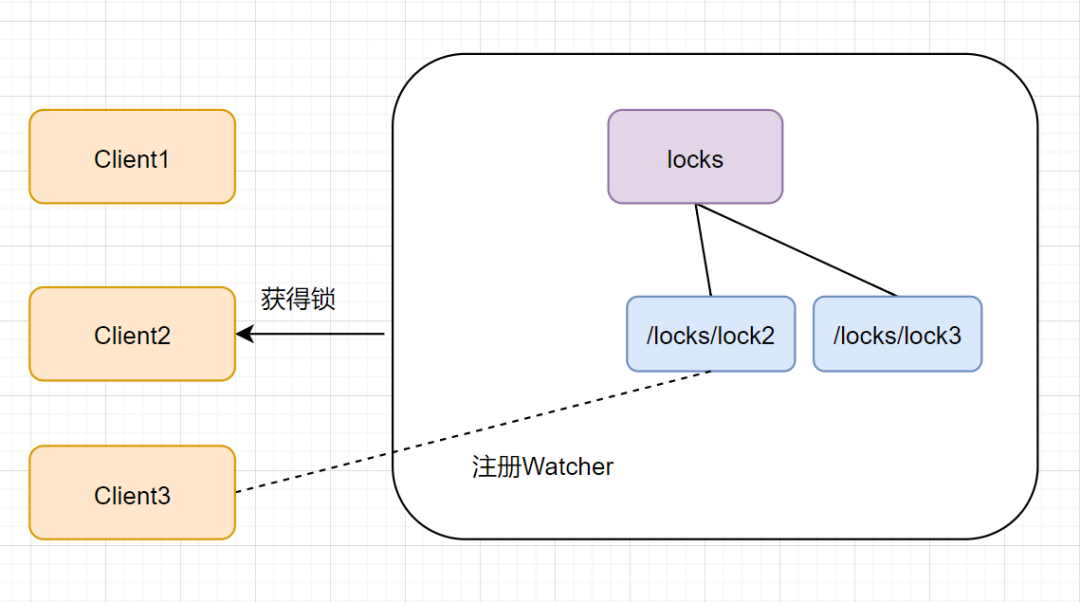
同理,Client2 获得锁之后,Client3 也对它虎视眈眈,啊哈哈~
效果
Zookeeper 保证了如下分布式一致性特性:
- 「顺序一致性」:从同一客户端发起的事务请求,最终将会严格地按照顺序被应用到 ZooKeeper 中去。
- 「原子性」:所有事务请求的处理结果在整个集群中所有机器上的应用情况是一致的,也就是说,要么整个集群中所有的机器都成功应用了某一个事务,要么都没有应用。
- 「单一视图」:无论客户端连到哪一个 ZooKeeper 服务器上,其看到的服务端数据模型都是一致的。
- 「可靠性」 :一旦服务端成功地应用了一个事务,并完成对客户端的响应,那么该事务所引起的服务端状态变更将会被一直保留下来。
- 「实时性(最终一致性)」: Zookeeper 仅仅能保证在一定的时间段内,客户端最终一定能够从服务端上读取到最新的数据状态。
1.8 zk 集群搭建
ZooKeeper 集群是一主多从的结构:
- 如果是写入数据,先写入主服务器(主节点),再通知从服务器。
- 如果是读取数据,既可以读主服务器的,也可以读从服务器的。
Zookeeper 是采用 ZAB 协议(Zookeeper Atomic Broadcast,Zookeeper 原子广播协议)来保证主从节点数据一致性的,ZAB 协议支持崩溃恢复和消息广播两种模式,很好解决了这两个问题:
- 崩溃恢复:Leader 挂了,进入该模式,选一个新的 leader 出来
- 消息广播: 把更新的数据,从 Leader 同步到所有 Follower
Leader 服务器挂了,所有集群中的服务器进入 LOOKING 状态,首先,它们会选举产生新的 Leader 服务器;接着,新的 Leader 服务器与集群中 Follower 服务进行数据同步,当集群中超过半数机器与该 Leader 服务器完成数据同步之后,退出恢复模式进入消息广播模式。Leader 服务器开始接收客户端的事务请求生成事务 Proposal 进行事务请求处理。
具体命令以后再说吧......
2. Spring Cloud Zookeeper
2.1 快速入门
准备事项
首先启动一个 zk 服务:
[zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 9] ls -R /
/
/zookeeper
/zookeeper/config
/zookeeper/quota
[zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 10]在一个 SpringBoot 项目中,直接引入下述依赖,即可启用 zookeeper 的服务注册与发现机制:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-zookeeper-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>微服务 1
例如,对于如下配置的一个 Spring Boot 应用,其在启动时会连接localhost:2181处的 zk 服务,同时将自己注册进去。
application.yml
server: port: 8081 spring: application: name: zk-client1 cloud: zookeeper: connect-string: localhost:2181主启动类:
@SpringBootApplication @RestController public class ZKClient1 { @GetMapping("/hello") public String sayHello() { return "Hello, I'm zk-client1, you find me!"; } public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ZKClient1.class, args); } }
项目启动后,再去观察 zk 的节点信息,会发下如下变化:
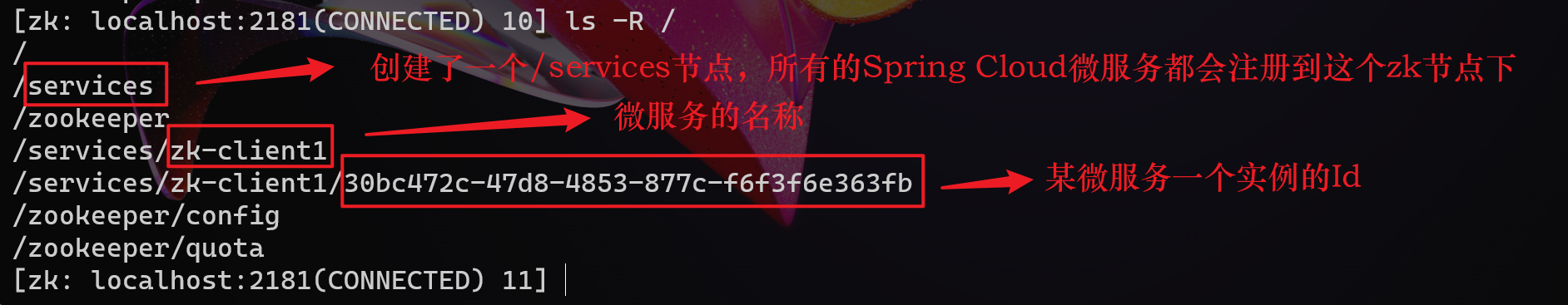
对于上述末级 zk 节点,其中存储了如下信息:
[zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 12] get /services/zk-client1/30bc472c-47d8-4853-877c-f6f3f6e363fb
{"name":"zk-client1","id":"30bc472c-47d8-4853-877c-f6f3f6e363fb","address":"RedmiBook-2021","port":8081,"sslPort":null,"payload":{"@class":"org.springframework.cloud.zookeeper.discovery.ZookeeperInstance","id":"zk-client1","name":"zk-client1","metadata":{"instance_status":"UP"}},"registrationTimeUTC":1677414164157,"serviceType":"DYNAMIC","uriSpec":{"parts":[{"value":"scheme","variable":true},{"value":"://","variable":false},{"value":"address","variable":true},{"value":":","variable":false},{"value":"port","variable":true}]}}其中的 json 数据格式化后如下:
{
"name": "zk-client1",
"id": "30bc472c-47d8-4853-877c-f6f3f6e363fb",
"address": "RedmiBook-2021",
"port": 8081,
"sslPort": null,
"payload": {
"@class": "org.springframework.cloud.zookeeper.discovery.ZookeeperInstance",
"id": "zk-client1",
"name": "zk-client1",
"metadata": {
"instance_status": "UP"
}
},
"registrationTimeUTC": 1677414164157,
"serviceType": "DYNAMIC",
"uriSpec": {
"parts": [
{
"value": "scheme",
"variable": true
},
{
"value": "://",
"variable": false
},
{
"value": "address",
"variable": true
},
{
"value": ":",
"variable": false
},
{
"value": "port",
"variable": true
}
]
}
}微服务 2
这里再创建第二个微服务zk-client2,来演示一下服务发现的过程:
application.yml
server: port: 8082 spring: application: name: zk-client2 cloud: zookeeper: connect-string: localhost:2181主启动类
@EnableFeignClients @SpringBootApplication public class ZKClient2 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ZKClient2.class, args); } }启动成功后的 zk 节点信息:
[zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 1] ls -R / / /services /zookeeper /services/zk-client1 /services/zk-client2 /services/zk-client1/30bc472c-47d8-4853-877c-f6f3f6e363fb /services/zk-client2/c2a58264-f8d4-455e-b03e-a9ca5e7783f6 /zookeeper/config /zookeeper/quotaFeign 客户端(可直接调通):
@FeignClient("zk-client1") public interface Zk1Client { @GetMapping("/hello") String sayHello(); }
2.2 服务注册
自动式
像快速入门中那样引入 maven 依赖就够了。
When a client registers with Zookeeper, it provides metadata (such as host and port, ID, and name) about itself.
The default service name, instance ID, and port (taken from the Environment) are ${spring.application.name}, the Spring Context ID, and ${server.port}, respectively.
Having spring-cloud-starter-zookeeper-discovery on the classpath makes the app into both a Zookeeper “service” (that is, it registers itself) and a “client” (that is, it can query Zookeeper to locate other services).
If you would like to disable the Zookeeper Discovery Client, you can set spring.cloud.zookeeper.discovery.enabled to false.
手动编程式
Spring Cloud Zookeeper implements the ServiceRegistry interface, letting developers register arbitrary services in a programmatic way.
The ServiceInstanceRegistration class offers a builder() method to create a Registration object that can be used by the ServiceRegistry, as shown in the following example:
@Autowired
private ZookeeperServiceRegistry serviceRegistry;
public void registerThings() {
ZookeeperRegistration registration = ServiceInstanceRegistration.builder()
.defaultUriSpec()
.address("anyUrl")
.port(10)
.name("/a/b/c/d/anotherservice")
.build();
this.serviceRegistry.register(registration);
}Instance Status
Netflix Eureka supports having instances that are OUT_OF_SERVICE registered with the server. These instances are not returned as active service instances. This is useful for behaviors such as blue/green deployments. (Note that the Curator Service Discovery recipe does not support this behavior.) Taking advantage of the flexible payload has let Spring Cloud Zookeeper implement OUT_OF_SERVICE by updating some specific metadata and then filtering on that metadata in the Spring Cloud LoadBalancer ZookeeperServiceInstanceListSupplier. The ZookeeperServiceInstanceListSupplier filters out all non-null instance statuses that do not equal UP. If the instance status field is empty, it is considered to be UP for backwards compatibility. To change the status of an instance, make a POST with OUT_OF_SERVICE to the ServiceRegistry instance status actuator endpoint, as shown in the following example:
$ http POST http://localhost:8081/service-registry status=OUT_OF_SERVICE2.3 服务发现
对于 Spring Cloud Zookeeper 而言,其要调用其他服务的 api 的话:
声明式:可以直接声明和使用对应的 feign 客户端,以被调方的服务名为名即可。此外也可以使用 Spring RestTemplate 和 Spring WebFlux。
Spring Cloud has support for Feign (a REST client builder), Spring
RestTemplateand Spring WebFlux, using logical service names instead of physical URLs.编程式:使用
org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.DiscoveryClient@Autowired private DiscoveryClient discoveryClient; @GetMapping("/{serviceId}") public List<ServiceInstance> getInstances(@PathVariable String serviceId) { return discoveryClient.getInstances(serviceId); }
2.4 负载均衡
Feign, Spring Cloud Gateway and Spring Cloud LoadBalancer all work with Spring Cloud Zookeeper.
Spring Cloud Zookeeper provides an implementation of Spring Cloud LoadBalancer ServiceInstanceListSupplier. When you use the spring-cloud-starter-zookeeper-discovery, Spring Cloud LoadBalancer is autoconfigured to use the ZookeeperServiceInstanceListSupplier by default.
2.5 设置依赖服务
Spring Cloud Zookeeper 可以通过配置来设置一个微服务所需要依赖的其他微服务,从而清晰化服务之间的依赖关系。此外,You can also use the Zookeeper Dependency Watchers functionality to control and monitor the state of your dependencies.
Including a dependency on org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-starter-zookeeper-discovery enables autoconfiguration that sets up Spring Cloud Zookeeper Dependencies. Even if you provide the dependencies in your properties, you can turn off the dependencies. To do so, set the spring.cloud.zookeeper.dependency.enabled property to false (it defaults to true).
配置项
设置依赖相关的配置项如下(以spring.cloud.zookeeper.dependencies打头):
spring.application.name: yourServiceName
spring.cloud.zookeeper:
dependencies:
newsletter: # 给依赖的微服务起个别名
path: /path/where/newsletter/has/registered/in/zookeeper
loadBalancerType: ROUND_ROBIN
contentTypeTemplate: application/vnd.newsletter.$version+json
version: v1
headers:
header1:
- value1
header2:
- value2
required: false
stubs: org.springframework:foo:stubs
mailing: # 给依赖的微服务起个别名
path: /path/where/mailing/has/registered/in/zookeeper
loadBalancerType: ROUND_ROBIN
contentTypeTemplate: application/vnd.mailing.$version+json
version: v1
required: truealias:Below the root property you have to represent each dependency as an alias. This is due to the constraints of Spring Cloud LoadBalancer, which requires that the application ID be placed in the URL. Consequently, you cannot pass any complex path, suchas/myApp/myRoute/name). The alias is the name you use instead of theserviceIdforDiscoveryClient,Feign, orRestTemplate. In the previous examples, the aliases arenewsletterandmailing.例如,我们改造一下快速入门中的微服务 2:
server: port: 8082 spring: application: name: zk-client2 cloud: zookeeper: connect-string: localhost:2181 dependencies: zk-client1-alias: # 别名 required: true # zk 中在 path 中未找到服务时,本项目启动会报错 path: /zk-client1在这种情况下,以下两个 Feign 客户端是等效的:
以被依赖服务的原服务名来匹配:
@FeignClient("zk-client1") public interface Zk1Client { @GetMapping("/hello") String sayHello(); }以被依赖服务的别名来匹配:
@FeignClient("zk-client1-alias") public interface Zk1AliasClient { @GetMapping("/hello") String sayHello(); }
path:The path is represented by thepathYAML property and is the path under which the dependency is registered under Zookeeper. As described in the previous section, Spring Cloud LoadBalancer operates on URLs. As a result, this path is not compliant with its requirement. That is why Spring Cloud Zookeeper maps the alias to the proper path.loadBalancerType:STICKY: Once chosen, the instance is always called.RANDOM: Picks an instance randomly.ROUND_ROBIN: Iterates over instances over and over again.
略了......
依赖监听
Spring Cloud Zookeeper Dependency Watcher.
The Dependency Watcher mechanism lets you register listeners to your dependencies. The functionality is, in fact, an implementation of the Observator pattern. When a dependency changes, its state (to either UP or DOWN), some custom logic can be applied.
org.springframework.cloud.zookeeper.discovery.watcher.DependencyWatcherListener and register it as a bean. The interface gives you one method:
void stateChanged(String dependencyName, DependencyState newState);If you want to register a listener for a particular dependency, the dependencyName would be the discriminator for your concrete implementation. newState provides you with information about whether your dependency has changed to CONNECTED or DISCONNECTED.
2.6 配置中心
Zookeeper provides a hierarchical namespace that lets clients store arbitrary data, such as configuration data. Spring Cloud Zookeeper Config is an alternative to the Config Server and Client. Configuration is loaded into the Spring Environment during the special “bootstrap” phase. Configuration is stored in the /config namespace by default. Multiple PropertySource instances are created, based on the application’s name and the active profiles, to mimic the Spring Cloud Config order of resolving properties. For example, an application with a name of testApp and with the dev profile has the following property sources created for it:
config/testApp,devconfig/testAppconfig/application,devconfig/application
The most specific property source is at the top, with the least specific at the bottom. Properties in the config/application namespace apply to all applications that use zookeeper for configuration. Properties in the config/testApp namespace are available only to the instances of the service named testApp.
Configuration is currently read on startup of the application. Sending a HTTP POST request to /refresh causes the configuration to be reloaded. Watching the configuration namespace (which Zookeeper supports) is not currently implemented.
Including a dependency on org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-starter-zookeeper-config enables autoconfiguration that sets up Spring Cloud Zookeeper Config.
更新日志
24bfd-于a357e-于899db-于eedbf-于c9215-于75141-于730b3-于21f41-于1e28c-于8755f-于
