heapq
关于heapq标准库:
>>> help(heapq)
Help on module heapq:
NAME
heapq - Heap queue algorithm (a.k.a. priority queue).
DESCRIPTION
Heaps are arrays for which a[k] <= a[2k+1] and a[k] <= a[2k+2] for
all k, counting elements from 0. For the sake of comparison,
non-existing elements are considered to be infinite. The interesting
property of a heap is that a[0] is always its smallest element.
Usage:
heap = [] # creates an empty heap
heappush(heap, item) # pushes a new item on the heap
item = heappop(heap) # pops the smallest item from the heap
item = heap[0] # smallest item on the heap without popping it
heapify(x) # transforms list into a heap, in-place, in linear time
item = heapreplace(heap, item) # pops and returns smallest item, and adds
# new item; the heap size is unchanged
Our API differs from textbook heap algorithms as follows:
- We use 0-based indexing. This makes the relationship between the
index for a node and the indexes for its children slightly less
obvious, but is more suitable since Python uses 0-based indexing.
- Our heappop() method returns the smallest item, not the largest.
These two make it possible to view the heap as a regular Python list
without surprises: heap[0] is the smallest item, and heap.sort()
maintains the heap invariant!
若要从一个容器中获取最大或者最小的N个元素组成的列表,可以通过heapq模块的nlargest()和nsmallest()解决这个问题(他们在底层实现里会对数据进行堆排序,时间复杂度仅仅是O(log N),N是堆大小)。

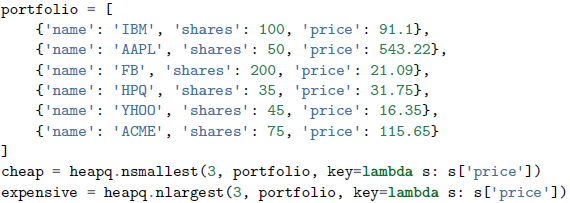
- 当要查找的元素个数相对较小时,函数
nlargest()和nsmallest()非常合适; - 若仅仅要查找唯一的最小或最大的元素的话,使用
min()和max()函数会更快些; - 如果N的大小和容器大小接近的话,通常先排序这个集合然后再使用切片操作会更快点。
使用heapq模块实现一个简单的优先级队列:
push()和pop()操作时间复杂度为O(log N),因此就算N很大其运算速度也很快。import heapq class PriorityQueue: def __init__(self): self._queue = [] self._index = 0 def push(self, item, priority): heapq.heappush(self._queue, (-priority, self._index, item)) self._index += 1 def pop(self): return heapq.heappop(self._queue)[-1]在上面的代码中,队列包含了一个(priority, index, item)的元组。index变量的作用是保证同等优先级元素的正确排序,通过保存一个不断增加的index下标变量,可以确保元素按照它们插入的顺序排序。
python在做元组比较时,如果前面的比较已经可以确定结果,后面的比较操作就不会发生了。
若有一些排序序列,想将它们合并而得到一个排序序列并在上面迭代遍历,使用heapq.merge()函数。见“迭代器”页面笔记。
更新日志
899db-于eedbf-于47fa5-于c9215-于75141-于730b3-于0e6a3-于29df4-于ff50e-于
